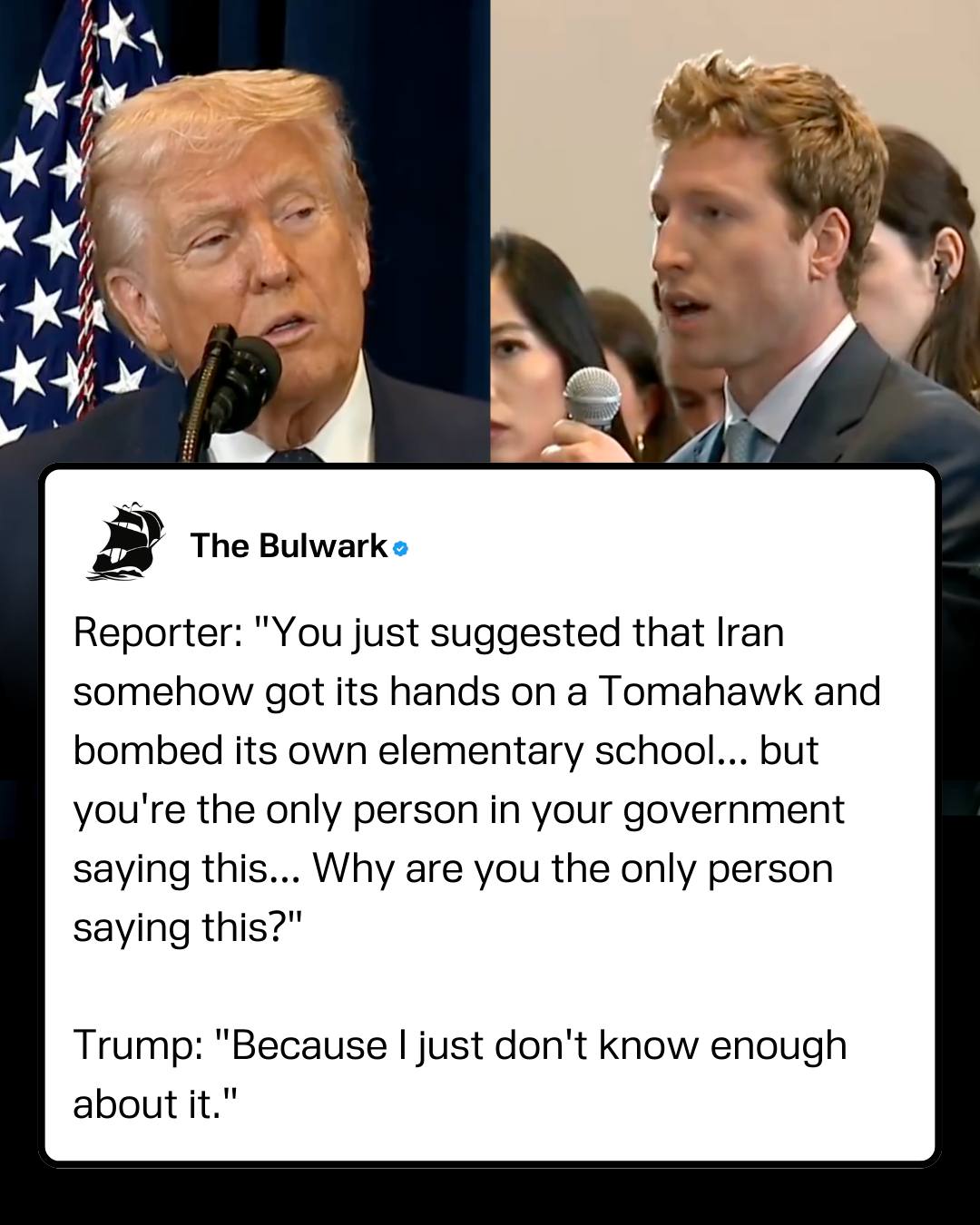
A White House reporter is being praised online after confronting Donald Trump during a press conference about the war with Iran.
Shawn McCreesh, a correspondent for The New York Times, challenged the president after Trump suggested that Iran may have bombed its own elementary school using a Tomahawk cruise missile.
McCreesh pushed back directly:
“You just suggested that Iran somehow got its hands on a Tomahawk and bombed its own elementary school… but you're the only person in your government saying this. Even your defense secretary wouldn't say that. Why are you the only person saying this?”
Trump replied: “Because I just don’t know enough about it.”
The exchange came as reporters pressed the administration about the deadly strike on the Shajareh Tayyebeh girls’ school in Minab, southern Iran, where around 160 people — many of them children — were reported killed during the early wave of attacks in the conflict.
Open-source investigators and journalists have since analyzed geolocated video and satellite imagery from the scene. One widely circulated clip appears to show a Tomahawk cruise missile striking a compound next to the school.
Tomahawks are long-range precision cruise missiles developed and primarily used by the United States, typically launched from U.S. Navy destroyers or submarines and capable of traveling hundreds of miles before striking a target with high accuracy. Iran is not known to possess Tomahawk systems, which is why the president’s suggestion immediately drew scrutiny in the briefing room.
The exchange quickly spread online, with many praising McCreesh for directly challenging the claim during a live White House press briefing.
Shawn McCreesh, a correspondent for The New York Times, challenged the president after Trump suggested that Iran may have bombed its own elementary school using a Tomahawk cruise missile.
McCreesh pushed back directly:
“You just suggested that Iran somehow got its hands on a Tomahawk and bombed its own elementary school… but you're the only person in your government saying this. Even your defense secretary wouldn't say that. Why are you the only person saying this?”
Trump replied: “Because I just don’t know enough about it.”
The exchange came as reporters pressed the administration about the deadly strike on the Shajareh Tayyebeh girls’ school in Minab, southern Iran, where around 160 people — many of them children — were reported killed during the early wave of attacks in the conflict.
Open-source investigators and journalists have since analyzed geolocated video and satellite imagery from the scene. One widely circulated clip appears to show a Tomahawk cruise missile striking a compound next to the school.
Tomahawks are long-range precision cruise missiles developed and primarily used by the United States, typically launched from U.S. Navy destroyers or submarines and capable of traveling hundreds of miles before striking a target with high accuracy. Iran is not known to possess Tomahawk systems, which is why the president’s suggestion immediately drew scrutiny in the briefing room.
The exchange quickly spread online, with many praising McCreesh for directly challenging the claim during a live White House press briefing.
A White House reporter is being praised online after confronting Donald Trump during a press conference about the war with Iran.
Shawn McCreesh, a correspondent for The New York Times, challenged the president after Trump suggested that Iran may have bombed its own elementary school using a Tomahawk cruise missile.
McCreesh pushed back directly:
“You just suggested that Iran somehow got its hands on a Tomahawk and bombed its own elementary school… but you're the only person in your government saying this. Even your defense secretary wouldn't say that. Why are you the only person saying this?”
Trump replied: “Because I just don’t know enough about it.”
The exchange came as reporters pressed the administration about the deadly strike on the Shajareh Tayyebeh girls’ school in Minab, southern Iran, where around 160 people — many of them children — were reported killed during the early wave of attacks in the conflict.
Open-source investigators and journalists have since analyzed geolocated video and satellite imagery from the scene. One widely circulated clip appears to show a Tomahawk cruise missile striking a compound next to the school.
Tomahawks are long-range precision cruise missiles developed and primarily used by the United States, typically launched from U.S. Navy destroyers or submarines and capable of traveling hundreds of miles before striking a target with high accuracy. Iran is not known to possess Tomahawk systems, which is why the president’s suggestion immediately drew scrutiny in the briefing room.
The exchange quickly spread online, with many praising McCreesh for directly challenging the claim during a live White House press briefing.